

The terraced house is one of the most familiar styles of home
in Neath (and the UK as a whole).
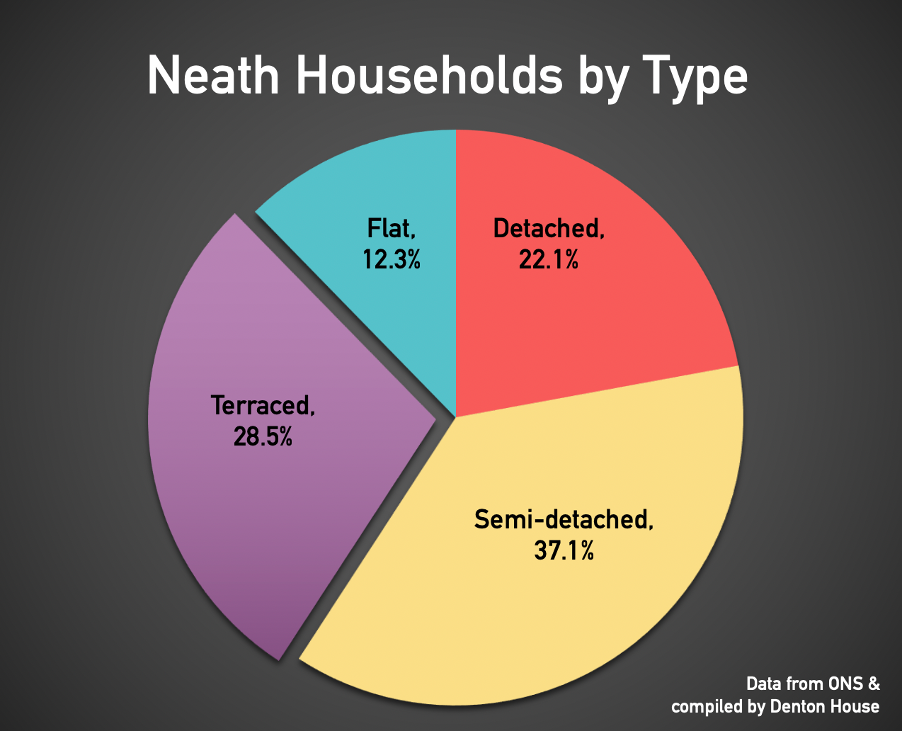
28.5% of Neath people live in a terraced home,
interesting when compared with the national average of 22.7%.
So, what is it about the humble terraced/townhouse us Brits
love so much? In this article, I look at the history of the terraced house, how
it relates to Neath and what the future holds for terraced homes.
A terraced house is a property built as part of a continuous
row of three (or more) properties in a similar and uniform style.
The reason the British call them ‘terraced houses’ and not ‘row houses’ came about because 18th century British architects borrowed the phrase ‘terrace’ from ‘terraced gardens’. Terraced gardens were known for their uniform nature (in looks, style and height etc.), so the architects decided to name them the same way as opposed to a ‘row house’. In fact, in most countries, they are called ‘row houses’.

The terraced house originated in the Low Countries of Europe in the late 1500s.
Terraced houses were first built en-masse in the UK after
the Great Fire of 1666 with the rebuilding of London.
They became fashionable for the landed gentry in the early
Georgian era with chic and stylish terraces appearing in London’s Mayfair and
Bath with its Queen Square (the forerunner of the famous Royal Crescent)
and were sometimes built around a garden square.
However, it wasn’t until the early 1800s that the terraced house
turned out to be the solution to the increasing population of the towns as more
and more people were attracted to towns and cities for work.
The terraced house fell out of favour with the upper-middle
classes in the late Victorian age (1870’s onwards) as they wanted more privacy
and space. They moved to live in detached houses or semi-detached villas, as
the terrace house had started to become associated with the lower-middle and
working classes.
With all these terraced houses being built, their quality of
construction and design dropped as builders tried to squeeze more profit. The
biggest issue was that most of the terraced houses built in the early to
mid-Victorian age (1840s to 1870s) were made back-to-back with no rear garden, causing
unsanitary conditions. Therefore, the Public Health Act of 1875 was introduced
to regulate the building of terraced houses with design and standards.
These new building standards in the Act improved the
terraced house’s ventilation and, more importantly, required the house to have a
toilet (frequently built outside). To meet these new building standards, the
designs of these new houses created the well-known landscape of ‘grid’ streets
lined with two-storey terraces serviced by a pedestrian path between them, the
name of which is a hotly debated topic. The various names for the pathway
include alleyway / jitty / cut/ ginnel / snicket / passageway / ten foot / five
foot/ witchel / lonnin / vennel.
As a Neath resident, why not say what you call them in the
comments?
As we entered the 20th Century, the terrace house continued
to be popular, albeit with some new architectural additions.
The advent of Arts and Craft architecture with stain glass
windows, Tudor style cladding, ornate porches, and elaborate chimney stacks.
After the First World War and the introduction of the
Housing and Town Planning Act 1919 (which made local councils build council
houses), the Victorian terraced rapidly became associated with overcrowding and
slums (especially those back-to-back terraced houses built before 1875). Many
of the back-to-back terraced houses were knocked down between 1930 and 1960 in
what is known as the slum clearances.
Private builders started building the iconic suburban
semi-detached houses with more extensive gardens, and local authorities decided
to build high-rise blocks after World War II. Yet after the partial collapse of
Ronan Point in 1968, the popularity of high-rise tower blocks waned.
Since the early 1990s though, the terraced house has
steadily come back into favour as building land prices have increased by 322%
in the last 30 years.
Many private builders have started to build modern
three-storey townhouses in rows of five to seven. This terraced
‘townhouse-style’ allows three and four bedrooms on a land footprint that would
have usually only accommodated a smaller two-bed property.
So, let’s look at some interesting stats on Neath terraced
houses.
- There are 6,245 terraced houses in Neath (broken
down as 4,360 privately owned terraced houses, 812 terraced council houses and 1,073
in the private rented sector)
- 17.2% of terraced houses in Neath are in the
private rented sector, which is below the national average of 19.1%
- The most expensive terraced house in Neath ever
sold was on Henfaes Road, Tonna, Neath for £753,000 in 2005
- The cheapest Neath terraced house sold in the
last two years was on Osbourne Street, a terraced house for £40,000
- Terraced houses in Neath sell for an average of £108
per square foot
I hope you found that thought-provoking?
So, why is the terraced house, be it a red brick Victorian
house or a more modern three-storey townhouse, still popular today in Neath?
They are typically well built, cheaper to maintain
(especially the older terraced houses), comparatively spacious, and in good locations.
Many terraced houses have been improved and extended through the inventive use
of rear gardens/yards and converted roof spaces; their unpretentious design
remains adaptable enough for 21st century living; what isn’t there to like
about them?
These are my thoughts; tell me your thoughts about the humble yet versatile Neath terraced house.




