- In 1981, 36.1%
of properties in Neath (and the Neath Port Talbot County Borough as a whole)
were council houses. Today, that figure stands at 12.4%, a proportional drop of
66%.
- Why has
the number of council houses dropped so much in those 40 years?
- How has
that changed the dynamics of the Neath property market in those 40 years?


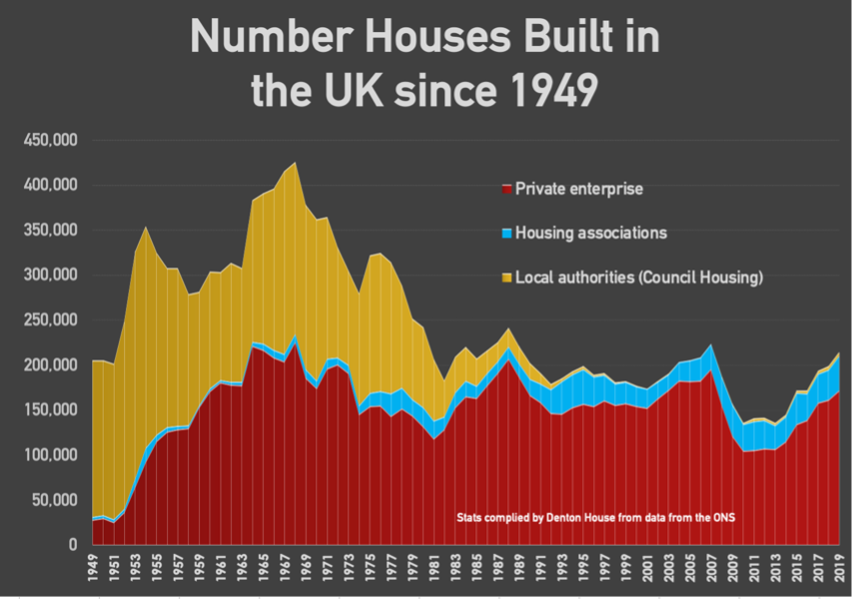
The ability of local authorities to build council houses came into
law in July 1919 with the 1919 Housing and Town Planning Act. It was one of the
most important pieces of domestic legislature passed after WW1 and was the
first time in the UK that a nationally public funded system of providing homes was
made for the masses. It was paid for mostly by central government and provided
by local authorities (councils) and public utility societies (which in later
years became today’s housing associations).
Between
1919 and 1979, 6.94 million council houses were built.
Just over 1 million council houses were built between 1920 and
1939, whilst 5,804,150 council houses were built between 1946 and 1979. This is
compared to 4,533,440 private homes and 260,910 housing association properties
in the same time frame (’46 to ’79).
So, between 1946 and 1979, the council house was the dominate
force of British housing. But that all changed in 1979!

Many people believe it was Margaret Thatcher who was
the architect of allowing the sitting tenant of a council house to buy their
home. Interestingly, council house tenants have been able to buy their council house
from as early as the mid 1930s, albeit with little or no discount. Also, as
late as 1977, the Labour Housing Minster published a Green Paper extolling the
virtues of homeownership and council tenants being able to buy their home at a
discount.
But after the General Election of 1979, the new Tory
government drafted the Housing Act 1980, which gave the Right to Buy, which became
law in the autumn of 1980. Then things really took off!
This new law established a right for most council
tenants who had been in their home for three years or more to a discount. The
discount started at 33% and increased by 1% for each extra year, up to a
maximum of 50%. If the tenant sold the house within the first five years of
ownership, a prorated repayment of their discount was required.
Between 1980 and 1989, 970,558 council houses nationally were sold at a discount.
Yet the issue was, when a council house was sold,
it took that house out of the council’s portfolio for future generations. From
the start, there were limitations on local authorities’ use of monies from the council
house sales as most of it had to be given to central government in London, meaning
only 390,560 new council houses were built between 1980 and 1989. Looking at
the numbers locally …
in 1981, there were 18,373 council houses in the Neath Port Talbot County Borough, today it’s 7,496.
No wonder the country has a housing
crisis … yet as my regular readers know – the devil is in the detail … and that
devil is the humble housing association.
The Tory General Election Manifesto in 1979 had
proposed the rights for both council house and housing association tenants to
buy their own house under the Right to Buy scheme. The Conservatives argued housing
associations, who obtained government funding, should be subject to the same Right
to Buy proposals as councils. The Government won the vote in the Commons, yet
lost the vote in the Lords, meaning housing association tenants could not buy
their homes at a large discount.
At the time, there were only 400,000 housing association
properties in the country, so the Government were not that worried. But the
significance of housing associations developed in the 1980s and beyond as they
were allowed to borrow money from the private sector.
Between 1949 and 1979, the average number of housing association
properties built annually was 8,524. Since 1979 to today, it has been 25,062
per year (and 31,606 per year in the 2010s).
Also, the Government encouraged councils to transfer
their remaining council houses to housing association schemes from 1986. The
advantage to these ‘stock transfers’ was the Government allowed housing associations
to access private funding to improve their existing properties and buy new ones
(good news for existing tenants complaining that the local authority never
upgraded their homes).
Moreover, the Tory Government liked stock transfers,
as it allowed them to dismantle council housing from the inside. Interestingly,
Labour expanded the ‘Stock Transfer’ process in 1997 and further reduced the eligibility
for council tenants’ Right to Buy, meaning the number of council tenants
exercising their Right to Buy declined considerably.
Meaning today, even though the provision of council
housing has dropped like the proverbial
stone …
the number of housing association properties in the Neath Port Talbot County Borough has increased from 326 in 1981 to 4,049.
So, how has this changed the dynamic of the Neath property market
in the last 40 years?
Would it surprise you to learn that the number of people who own
their own Neath home today is very similar to what it was 20 years ago before
the property boom started? It’s just that even though we’ve had a large drop in
the number of council houses and an increase in the number of housing
association properties, the number of people owning their own home has remained
relatively the same (in some areas of Neath this has actually increased), the
significant issue is the growth of the private rented sector.
It’s almost as if people who used to rent from the council now rent from a private landlord.
The question is, is it right for private individuals to make money
from tenants who rent from them as opposed to the local authority? Or are
private landlords providing better types, choices and quality of accommodation
for these tenants, albeit at a higher rental rate than if they rented a council
house?
I really do believe if it wasn’t for the growth of the buy-to-let
landlord, which began in the early 2000s, we would have an even bigger housing
crisis on our hands than the one we have currently.
Both local and central government have had their hands tied behind
their backs since 2008 with a lack of funding, and it’s the humble private
landlord who has stepped up and supplied in excess of 2.3million additional rental
properties since 2001, housing nearly 5,520,000 Brits. These landlords have
saved the day since the big council house sell off in the 1980s!
What are your thoughts on this matter?
If you’ve got any questions about buying, selling or letting property in South Wales, speak to our local property experts today!




